The Future of Social Media: A Blockchain-Driven Transformation
Introduction
The advent of social media has significantly impacted the way people communicate and engage with each other globally. Since the earliest social networks, platforms have continuously evolved to cater to changing user needs and preferences. However, the current generation of social media has faced various challenges, including privacy concerns and centralized control. This article delves into the history of social media, its monetization models, and how blockchain technology is revolutionizing the industry by creating better social media apps.
History of Social Media
The roots of social media can be traced back to the 1990s, with platforms such as SixDegrees.com, which allowed users to create profiles, list friends, and connect with others. The concept of social networking rapidly evolved with the emergence of Friendster in 2002, MySpace in 2003, and Facebook in 2004. These platforms gained popularity by leveraging the power of network effects, where the value of a service increases as more people join and participate.
The proliferation of smartphones and mobile internet access further fueled the growth of social media. Platforms like Twitter, Instagram, and Snapchat emerged, each offering unique features tailored to different user preferences. Today, social media platforms have grown into massive global communities, with billions of users sharing, liking, and engaging in real-time conversations.
As the internet evolved, online forums and chat rooms facilitated social interactions and laid the foundation for modern social media. IRC (Internet Relay Chat), Usenet, and AOL Instant Messenger were some of the earliest platforms for online communication. However, these platforms lacked user-friendly interfaces and features found in contemporary social networks.
With the launch of LiveJournal in 1999, users could create blogs and interact with others through comments, paving the way for more interactive social media platforms. As broadband internet became more accessible, multimedia sharing websites like Flickr (2004) and YouTube (2005) gained popularity, allowing users to share photos and videos with a global audience.
As smartphones became ubiquitous, social media platforms adapted to mobile usage. Instagram (2010) and Snapchat (2011) capitalized on the growing trend of sharing visual content through mobile devices, further expanding the social media landscape.
Monetization Models
The primary monetization model for social media platforms has been advertising. Platforms collect user data, analyze their preferences, and display targeted ads to generate revenue. This model has been lucrative for companies like Facebook and Google, which dominate the online advertising space.
However, this model has also led to several disadvantages. Centralized control of user data poses privacy risks, as platforms have the power to control, manipulate, or sell user information. The ad-driven model can also lead to content manipulation, promoting sensationalism and clickbait to increase engagement and ad revenue, often at the expense of quality and authenticity.
Apart from advertising, other monetization models have emerged in the social media space:
Subscription-based models: Some platforms offer premium features, such as ad-free experiences, exclusive content, or advanced analytics, for a monthly or annual fee. Examples include LinkedIn Premium and YouTube Premium.
In-app purchases and virtual goods: Platforms like TikTok and Snapchat enable users to purchase virtual goods, such as stickers, filters, or coins, to enhance their experiences or support creators.
Creator monetization: Social media platforms have introduced features to help creators monetize their content, such as Patreon’s subscription-based support, YouTube’s Super Chat, and Instagram’s shoppable posts.
Data monetization: Although controversial, some platforms have monetized user data by selling it to third parties for research or marketing purposes.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Current Social Media Platforms
Current social media platforms offer numerous advantages, such as enabling global communication, fostering communities, and supporting content sharing. These platforms have democratized access to information and allowed people to express themselves and connect with others.
However, there are also several drawbacks, such as privacy concerns, mental health impacts, and the spread of misinformation. Users often have little control over their data, leading to increasing demands for more transparent and decentralized solutions.
Advantages:
Economic opportunities: Social media platforms have created new economic opportunities for businesses, entrepreneurs, and creators to promote their products, services, and content.
Advocacy and awareness: Social media enables users to raise awareness for causes, mobilize support, and facilitate political activism.
Education and learning: Many platforms, such as YouTube and LinkedIn, offer educational content and professional development resources.
Real-time updates: Social media provides instant access to news, events, and updates from around the world.
Disadvantages:
Cyberbullying and harassment: Social media platforms can facilitate cyberbullying, harassment, and trolling, negatively affecting users’ mental health and well-being.
Addiction and mental health: Excessive social media use has been linked to increased rates of depression, anxiety, and feelings of isolation.
Echo chambers and polarization: Algorithms used by social media platforms can create echo chambers, where users are exposed to content that reinforces their beliefs, potentially contributing to social and political polarization.
Censorship and content moderation: Content moderation policies can lead to censorship, stifling free speech and suppressing marginalized voices.
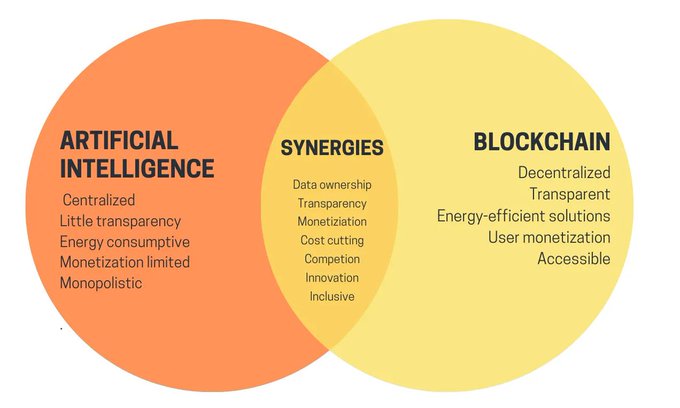
Web 3.0 and Blockchain-Driven Social Networks
Web 3.0 represents a paradigm shift towards a decentralized internet, where users have more control over their data and interactions. Blockchain technology plays a crucial role in this transformation, as it enables the creation of decentralized applications (dApps) and protocols to build better social media platforms.
By leveraging blockchain technology, social media platforms can empower users to own their data and have the freedom to transfer it from one dApp to another. This approach eliminates centralized control, reducing the risk of privacy breaches and manipulation. Furthermore, decentralized social networks can adopt alternative monetization models, such as token-based economies, which reward users for their contributions and engagement.
Emerging Blockchain Protocols
Several protocols are being developed to pave the way for decentralized social media, including Lens Protocol, Farcaster, and Deso.
Lens Protocol: Lens Protocol is a decentralized protocol for building social media dApps with an emphasis on user privacy and content ownership. It uses end-to-end encryption and a decentralized storage system to ensure that users have complete control over their data.
Farcaster: Farcaster is a decentralized social media protocol focused on content monetization. It enables users to create, curate, and monetize content through tokenization, allowing them to earn rewards for their contributions and engagement.
Deso: Deso (Decentralized Social) is an open-source protocol and blockchain platform that allows developers to build decentralized social networks. Deso features a native cryptocurrency, which can be used to reward users for their engagement and facilitate transactions within the ecosystem. By providing a decentralized infrastructure, Deso aims to foster a more equitable and user-centric social media landscape.
The Convergence of Blockchain, AI, and VR/AR in Social Networking
As technology continues to advance, the integration of blockchain, artificial intelligence (AI), and virtual reality/augmented reality (VR/AR) will redefine social networking. Decentralized virtual experiences will become more immersive and interactive, as users navigate digital spaces that adapt to their preferences and behaviors.
AI will facilitate content personalization, moderation, and real-time translation, enhancing communication and collaboration across diverse user groups across different languages. AI-driven algorithms can also help combat misinformation and malicious content more effectively, while still maintaining decentralization and user privacy.
VR/AR technology will further revolutionize social media experiences by enabling users to engage in immersive, shared virtual environments. These technologies can foster deeper connections, as users interact with each other’s avatars, attend virtual events, or explore digital worlds together. The combination of VR/AR, AI, and blockchain will give rise to new business models, such as virtual real estate, digital goods, and experiences that can be owned, traded, or monetized on decentralized marketplaces.
Blockchain technology will ensure that all interactions within these immersive environments are recorded securely and transparently. This guarantees the provenance of digital assets and allows users to maintain control over their data, even as they engage in increasingly complex virtual experiences.
In conclusion, the future of social networking will be shaped by the convergence of blockchain, AI, and VR/AR technologies. By leveraging these innovations, social media platforms can address current challenges, such as privacy concerns, data ownership, and content moderation, while also delivering richer, more engaging experiences for users. As the boundaries between the physical and digital worlds continue to blur, decentralized social media platforms will play a vital role in facilitating seamless and secure interactions in the metaverse, fostering global communication, and empowering users to shape their digital identities.
The Future of Social Media: A Blockchain-Driven Transformation
Introduction
The advent of social media has significantly impacted the way people communicate and engage with each other globally. Since the earliest social networks, platforms have continuously evolved to cater to changing user needs and preferences. However, the current generation of social media has faced various challenges, including privacy concerns and centralized control. This article delves into the history of social media, its monetization models, and how blockchain technology is revolutionizing the industry by creating better social media apps.
History of Social Media
The roots of social media can be traced back to the 1990s, with platforms such as SixDegrees.com, which allowed users to create profiles, list friends, and connect with others. The concept of social networking rapidly evolved with the emergence of Friendster in 2002, MySpace in 2003, and Facebook in 2004. These platforms gained popularity by leveraging the power of network effects, where the value of a service increases as more people join and participate.
The proliferation of smartphones and mobile internet access further fueled the growth of social media. Platforms like Twitter, Instagram, and Snapchat emerged, each offering unique features tailored to different user preferences. Today, social media platforms have grown into massive global communities, with billions of users sharing, liking, and engaging in real-time conversations.
As the internet evolved, online forums and chat rooms facilitated social interactions and laid the foundation for modern social media. IRC (Internet Relay Chat), Usenet, and AOL Instant Messenger were some of the earliest platforms for online communication. However, these platforms lacked user-friendly interfaces and features found in contemporary social networks.
With the launch of LiveJournal in 1999, users could create blogs and interact with others through comments, paving the way for more interactive social media platforms. As broadband internet became more accessible, multimedia sharing websites like Flickr (2004) and YouTube (2005) gained popularity, allowing users to share photos and videos with a global audience.
As smartphones became ubiquitous, social media platforms adapted to mobile usage. Instagram (2010) and Snapchat (2011) capitalized on the growing trend of sharing visual content through mobile devices, further expanding the social media landscape.
Monetization Models
The primary monetization model for social media platforms has been advertising. Platforms collect user data, analyze their preferences, and display targeted ads to generate revenue. This model has been lucrative for companies like Facebook and Google, which dominate the online advertising space.
However, this model has also led to several disadvantages. Centralized control of user data poses privacy risks, as platforms have the power to control, manipulate, or sell user information. The ad-driven model can also lead to content manipulation, promoting sensationalism and clickbait to increase engagement and ad revenue, often at the expense of quality and authenticity.
Apart from advertising, other monetization models have emerged in the social media space:
Subscription-based models: Some platforms offer premium features, such as ad-free experiences, exclusive content, or advanced analytics, for a monthly or annual fee. Examples include LinkedIn Premium and YouTube Premium.
In-app purchases and virtual goods: Platforms like TikTok and Snapchat enable users to purchase virtual goods, such as stickers, filters, or coins, to enhance their experiences or support creators.
Creator monetization: Social media platforms have introduced features to help creators monetize their content, such as Patreon’s subscription-based support, YouTube’s Super Chat, and Instagram’s shoppable posts.
Data monetization: Although controversial, some platforms have monetized user data by selling it to third parties for research or marketing purposes.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Current Social Media Platforms
Current social media platforms offer numerous advantages, such as enabling global communication, fostering communities, and supporting content sharing. These platforms have democratized access to information and allowed people to express themselves and connect with others.
However, there are also several drawbacks, such as privacy concerns, mental health impacts, and the spread of misinformation. Users often have little control over their data, leading to increasing demands for more transparent and decentralized solutions.
Advantages:
Economic opportunities: Social media platforms have created new economic opportunities for businesses, entrepreneurs, and creators to promote their products, services, and content.
Advocacy and awareness: Social media enables users to raise awareness for causes, mobilize support, and facilitate political activism.
Education and learning: Many platforms, such as YouTube and LinkedIn, offer educational content and professional development resources.
Real-time updates: Social media provides instant access to news, events, and updates from around the world.
Disadvantages:
Cyberbullying and harassment: Social media platforms can facilitate cyberbullying, harassment, and trolling, negatively affecting users’ mental health and well-being.
Addiction and mental health: Excessive social media use has been linked to increased rates of depression, anxiety, and feelings of isolation.
Echo chambers and polarization: Algorithms used by social media platforms can create echo chambers, where users are exposed to content that reinforces their beliefs, potentially contributing to social and political polarization.
Censorship and content moderation: Content moderation policies can lead to censorship, stifling free speech and suppressing marginalized voices.
Web 3.0 and Blockchain-Driven Social Networks
Web 3.0 represents a paradigm shift towards a decentralized internet, where users have more control over their data and interactions. Blockchain technology plays a crucial role in this transformation, as it enables the creation of decentralized applications (dApps) and protocols to build better social media platforms.
By leveraging blockchain technology, social media platforms can empower users to own their data and have the freedom to transfer it from one dApp to another. This approach eliminates centralized control, reducing the risk of privacy breaches and manipulation. Furthermore, decentralized social networks can adopt alternative monetization models, such as token-based economies, which reward users for their contributions and engagement.
Emerging Blockchain Protocols
Several protocols are being developed to pave the way for decentralized social media, including Lens Protocol, Farcaster, and Deso.
Lens Protocol: Lens Protocol is a decentralized protocol for building social media dApps with an emphasis on user privacy and content ownership. It uses end-to-end encryption and a decentralized storage system to ensure that users have complete control over their data.
Farcaster: Farcaster is a decentralized social media protocol focused on content monetization. It enables users to create, curate, and monetize content through tokenization, allowing them to earn rewards for their contributions and engagement.
Deso: Deso (Decentralized Social) is an open-source protocol and blockchain platform that allows developers to build decentralized social networks. Deso features a native cryptocurrency, which can be used to reward users for their engagement and facilitate transactions within the ecosystem. By providing a decentralized infrastructure, Deso aims to foster a more equitable and user-centric social media landscape.
The Convergence of Blockchain, AI, and VR/AR in Social Networking
As technology continues to advance, the integration of blockchain, artificial intelligence (AI), and virtual reality/augmented reality (VR/AR) will redefine social networking. Decentralized virtual experiences will become more immersive and interactive, as users navigate digital spaces that adapt to their preferences and behaviors.
AI will facilitate content personalization, moderation, and real-time translation, enhancing communication and collaboration across diverse user groups across different languages. AI-driven algorithms can also help combat misinformation and malicious content more effectively, while still maintaining decentralization and user privacy.
VR/AR technology will further revolutionize social media experiences by enabling users to engage in immersive, shared virtual environments. These technologies can foster deeper connections, as users interact with each other’s avatars, attend virtual events, or explore digital worlds together. The combination of VR/AR, AI, and blockchain will give rise to new business models, such as virtual real estate, digital goods, and experiences that can be owned, traded, or monetized on decentralized marketplaces.
Blockchain technology will ensure that all interactions within these immersive environments are recorded securely and transparently. This guarantees the provenance of digital assets and allows users to maintain control over their data, even as they engage in increasingly complex virtual experiences.
In conclusion, the future of social networking will be shaped by the convergence of blockchain, AI, and VR/AR technologies. By leveraging these innovations, social media platforms can address current challenges, such as privacy concerns, data ownership, and content moderation, while also delivering richer, more engaging experiences for users. As the boundaries between the physical and digital worlds continue to blur, decentralized social media platforms will play a vital role in facilitating seamless and secure interactions in the metaverse, fostering global communication, and empowering users to shape their digital identities.
Continue reading
Continue reading

The Future of Social Media: A Blockchain-Driven Transformation
Apr 20, 2023

The Future of Social Media: A Blockchain-Driven Transformation
Apr 20, 2023