Decentralized Perp Exchanges
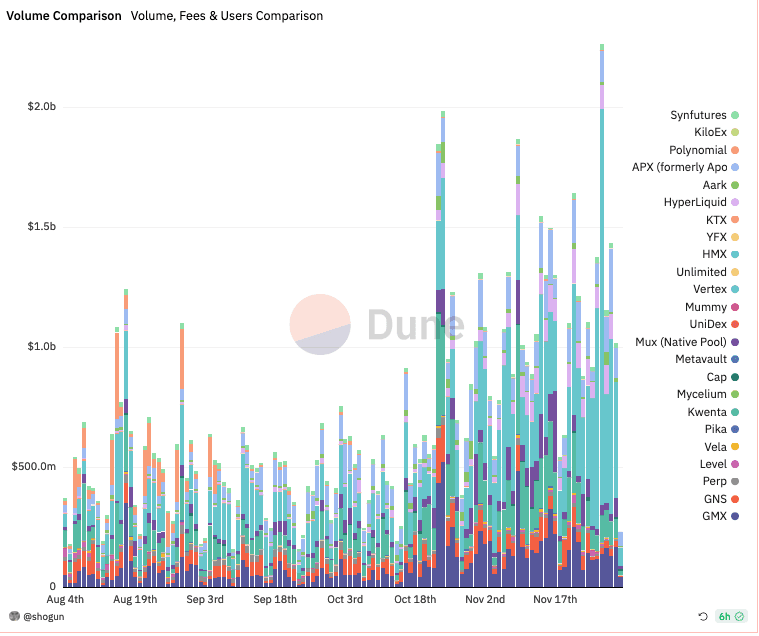
Perpetuals, also known as 'perps', are a type of financial instrument that allows traders to swap the value or cash flows of one asset for another indefinitely. While these instruments have traditionally been available on centralized exchanges like Binance and FTX, there has been a recent surge in decentralized perpetual exchanges, or 'perp dexes'.
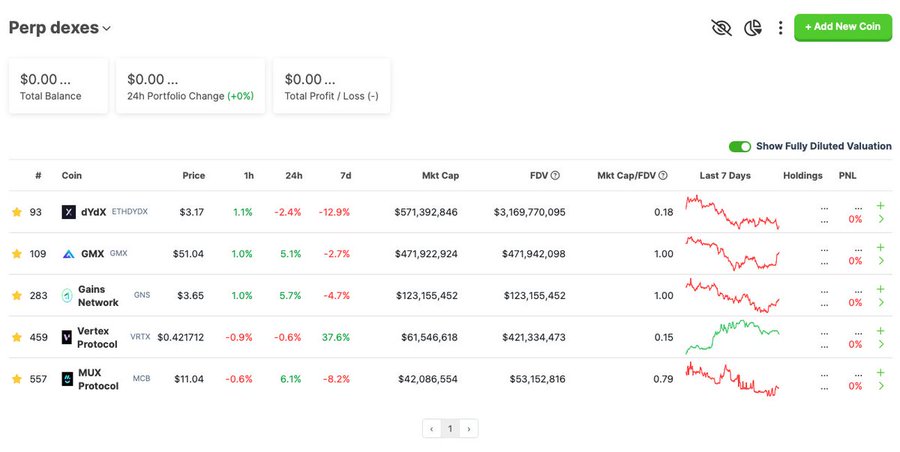
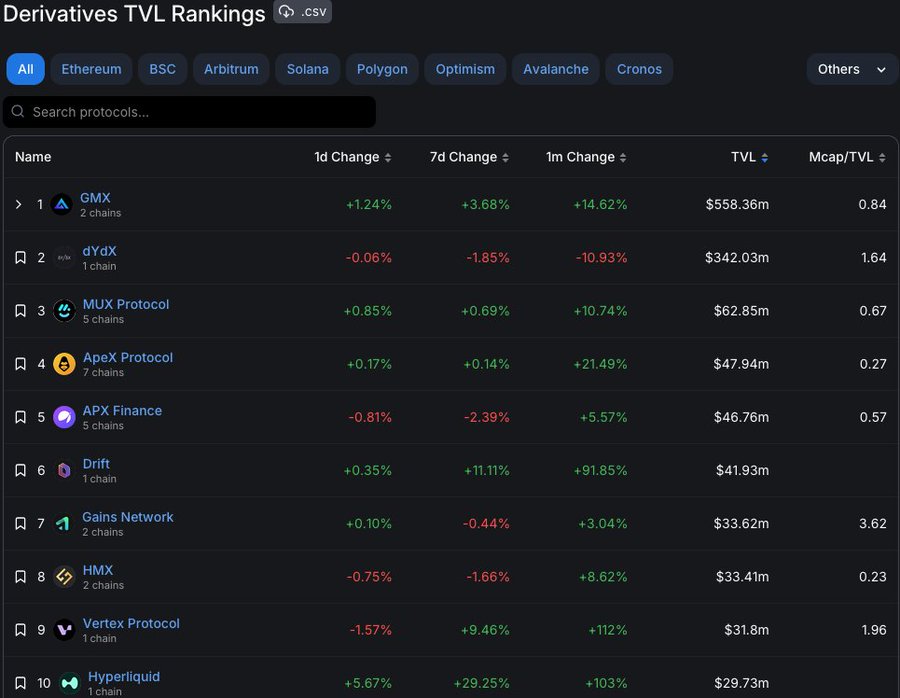
One of the largest perp dexes is GMX, which offers low swap fees and zero price impact thanks to the use of Chainlink oracles to provide secure pricing information for its order book. GMX has been deployed on both the Arbitrum and Avalanche chains, and utilizes a unique two-token model comprising of $GMX and $GLP. Market makers can provide liquidity to a multi-asset automated market maker (AMM) pool in exchange for $GLP tokens, which earn a share of platform fees paid out in either ETH or AVAX. $GMX can be staked to earn a share of platform fees in both ETH and AVAX, and is also used for governance.
Perpetual Protocol offers perp trading on 17 different cryptocurrencies with up to 10x leverage. Its v2 protocol, which has been deployed on Optimism, uses Uniswap v3's concentrated liquidity pools to allow market makers to provide liquidity in pairs to synthetic asset pools. Traders can then access these pools using Perpetual Protocol after providing collateral, such as USDC, ETH, or WETH. The $PERP token was initially used as a reward for market makers or as a gas rebate token for traders, but now has additional utility through veTokenomics and the use of vePerp, including voting power on the distribution of $PERP rewards and a share of referral rewards.
Other notable perp dex protocols include Gains Network, which has a market cap of $108.26 million and a fully diluted valuation (FDV) of $372.07 million, and Cap Dot Finance, with a market cap of $12.05 million and an FDV of $14.46 million.
It is important to note that while perpetuals can create immense wealth rapidly, they can also be risky if used unwisely. Traders should carefully consider the risks and ensure they fully understand how these instruments work before using them.
Undercollateralized Lending
Decentralized finance (DeFi) has the potential to revolutionize the traditional banking and credit system, with lending and borrowing being a crucial component. There are four pillars of the emerging on-chain financial system: lending and borrowing (such as with Aave), liquidity (like with Uniswap), stablecoin issuance (such as with MakerDAO), and wealth management (like with Loch Chain).
Borrowing in the real world refers to access to credit, or "money that you do not have". Loans can be classified based on two variables: the degree of collateralization (over or under) and the use of the loan (general or specific). This leads to four quadrants that traditional finance fully supports.
However, DeFi does not offer access to all four quadrants. It can easily handle over-collateralized loans, with protocols like Aave and Compound Finance seeing significant growth in total value locked over the past few years. On the other hand, under-collateralized lending is more challenging to solve in DeFi.
Why does under-collateralization matter? General purpose credit is crucial for an economy to stimulate consumption and economic growth. It creates liquidity using the fractional banking system, which is only possible in an under-collateralized system.
There are two main challenges to solving under-collateralized lending in DeFi: the inherent privacy of the system and the fragmentation of identity. Wallets are not linked to identity, and the fragmentation of identity incentivizes taking out loans on behalf of disposable entities and then defaulting without impacting creditworthiness.
There are two approaches being used to solve this issue: establishing closed systems with a prime brokerage, and real-world mapping with on-chain identity. Prime brokerages keep the reliance on "code is law" but flip the constraints by restricting the use of funds within a closed system. This allows them to control where borrowed funds are deployed and manage their risk accordingly. Protocols that use this approach include Oxygen Protocol, Delta Prime, and Gearbox Protocol.
The second approach, real-world mapping, involves imposing broader consequences for the borrower off-chain in order to ensure that the net losses from defaulting outweigh the immediate gains. This can be achieved using an on-chain version of know your customer (KYC). As long as there is at least one participant able to attest to the borrower's identity and one willing to underwrite the loan, there is no need to disclose the borrower's identity. Protocols that use this approach include Goldfinch and TrueFi.
When comparing these three approaches to DeFi lending, there are several basic properties to consider, including the security guarantee, the effect on borrower liquidity, borrower identity, and the uses of credit. Scalability is also an important factor, driven by system complexity, network effects, quality, and the ability to scale with demand.
Finally, DeFi lending and borrowing is still in its early stages, but it has the potential to significantly transform the current financial system and create a more transparent and capital-efficient system. It is an exciting space with a lot of potential for growth and innovation.
Sources:
https://jumpcrypto.com/paradigms-for-on-chain-credit/
https://dune.com/shogun/perpetual-dexs-overview
https://rileygmi.substack.com/p/gmx
https://tokenomicsdao.substack.com/p/tokenomics-101-perpetual-protocol
https://alphapls.substack.com/p/defi-gns-gmx-perp-leverage-trading-protocol
Decentralized Perp Exchanges
Perpetuals, also known as 'perps', are a type of financial instrument that allows traders to swap the value or cash flows of one asset for another indefinitely. While these instruments have traditionally been available on centralized exchanges like Binance and FTX, there has been a recent surge in decentralized perpetual exchanges, or 'perp dexes'.
One of the largest perp dexes is GMX, which offers low swap fees and zero price impact thanks to the use of Chainlink oracles to provide secure pricing information for its order book. GMX has been deployed on both the Arbitrum and Avalanche chains, and utilizes a unique two-token model comprising of $GMX and $GLP. Market makers can provide liquidity to a multi-asset automated market maker (AMM) pool in exchange for $GLP tokens, which earn a share of platform fees paid out in either ETH or AVAX. $GMX can be staked to earn a share of platform fees in both ETH and AVAX, and is also used for governance.
Perpetual Protocol offers perp trading on 17 different cryptocurrencies with up to 10x leverage. Its v2 protocol, which has been deployed on Optimism, uses Uniswap v3's concentrated liquidity pools to allow market makers to provide liquidity in pairs to synthetic asset pools. Traders can then access these pools using Perpetual Protocol after providing collateral, such as USDC, ETH, or WETH. The $PERP token was initially used as a reward for market makers or as a gas rebate token for traders, but now has additional utility through veTokenomics and the use of vePerp, including voting power on the distribution of $PERP rewards and a share of referral rewards.
Other notable perp dex protocols include Gains Network, which has a market cap of $108.26 million and a fully diluted valuation (FDV) of $372.07 million, and Cap Dot Finance, with a market cap of $12.05 million and an FDV of $14.46 million.
It is important to note that while perpetuals can create immense wealth rapidly, they can also be risky if used unwisely. Traders should carefully consider the risks and ensure they fully understand how these instruments work before using them.
Undercollateralized Lending
Decentralized finance (DeFi) has the potential to revolutionize the traditional banking and credit system, with lending and borrowing being a crucial component. There are four pillars of the emerging on-chain financial system: lending and borrowing (such as with Aave), liquidity (like with Uniswap), stablecoin issuance (such as with MakerDAO), and wealth management (like with Loch Chain).
Borrowing in the real world refers to access to credit, or "money that you do not have". Loans can be classified based on two variables: the degree of collateralization (over or under) and the use of the loan (general or specific). This leads to four quadrants that traditional finance fully supports.
However, DeFi does not offer access to all four quadrants. It can easily handle over-collateralized loans, with protocols like Aave and Compound Finance seeing significant growth in total value locked over the past few years. On the other hand, under-collateralized lending is more challenging to solve in DeFi.
Why does under-collateralization matter? General purpose credit is crucial for an economy to stimulate consumption and economic growth. It creates liquidity using the fractional banking system, which is only possible in an under-collateralized system.
There are two main challenges to solving under-collateralized lending in DeFi: the inherent privacy of the system and the fragmentation of identity. Wallets are not linked to identity, and the fragmentation of identity incentivizes taking out loans on behalf of disposable entities and then defaulting without impacting creditworthiness.
There are two approaches being used to solve this issue: establishing closed systems with a prime brokerage, and real-world mapping with on-chain identity. Prime brokerages keep the reliance on "code is law" but flip the constraints by restricting the use of funds within a closed system. This allows them to control where borrowed funds are deployed and manage their risk accordingly. Protocols that use this approach include Oxygen Protocol, Delta Prime, and Gearbox Protocol.
The second approach, real-world mapping, involves imposing broader consequences for the borrower off-chain in order to ensure that the net losses from defaulting outweigh the immediate gains. This can be achieved using an on-chain version of know your customer (KYC). As long as there is at least one participant able to attest to the borrower's identity and one willing to underwrite the loan, there is no need to disclose the borrower's identity. Protocols that use this approach include Goldfinch and TrueFi.
When comparing these three approaches to DeFi lending, there are several basic properties to consider, including the security guarantee, the effect on borrower liquidity, borrower identity, and the uses of credit. Scalability is also an important factor, driven by system complexity, network effects, quality, and the ability to scale with demand.
Finally, DeFi lending and borrowing is still in its early stages, but it has the potential to significantly transform the current financial system and create a more transparent and capital-efficient system. It is an exciting space with a lot of potential for growth and innovation.
Sources:
https://jumpcrypto.com/paradigms-for-on-chain-credit/
https://dune.com/shogun/perpetual-dexs-overview
https://rileygmi.substack.com/p/gmx
https://tokenomicsdao.substack.com/p/tokenomics-101-perpetual-protocol
https://alphapls.substack.com/p/defi-gns-gmx-perp-leverage-trading-protocol
Continue reading
Continue reading

Perp Exchanges AND Undercollateralized Lending
Nov 4, 2022

Perp Exchanges AND Undercollateralized Lending
Nov 4, 2022